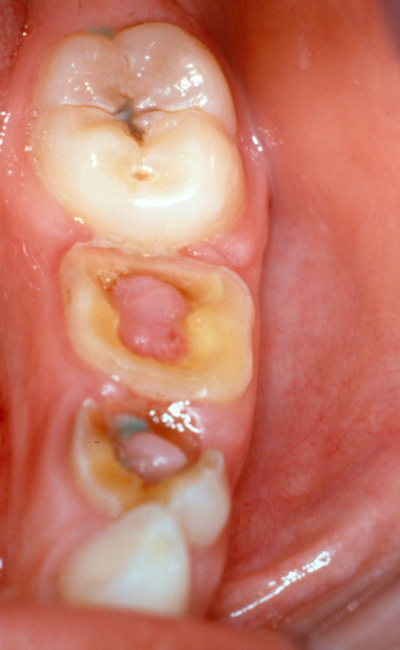
Oral piercing may cause different types of complication in the people. It puts a risk to the dental health of the people. Once oral piercing is done, the chances of infection also increase in the area which is pierced. Different kinds of bacteria always remain present in the mouth. When blood vessels present in the tongue are damaged due to piercing, they may bleed in excessive amounts. This may cause excessive loss of blood. Swelling usually occurs after oral piercing is done. It becomes difficult to heal the effects of piercing because tongue is used a lot for different functions. In some cases, swelling may cause hindrance to the breathing process. The risk of different blood borne disease like hepatitis C, B, D, G and tetanus also increases after oral piercing.
When people have barbells fitted in to their tongue they tend to tap it again and again on teeth and gums. This may lead to broken teeth and gum diseases. A large number of people who have oral piercing usually come up with some kind of infection in their gums. The infection which may be caused to the blood vessels which are connected to brain and other crucial parts of body, may even take one’s life. If you search the internet you can get to know about such cases. In case unsterile instruments are used for piercing the tongue, cheek or lips, it may cause HIV or AIDS. If you have to get oral piercing done then visiting a reputable clinic will be the best option.

 Causes:
Causes: